Computing multiple spectrograms with the Public API [1]#
As always in the Public API, the first step is to build the dataset.
Since we don’t know (nor we care about) the files begin timestamps, we’ll set the striptime_format to None, which will assign a default timestamp at which the first valid audio file will be considered to start. Then, each next valid audio file will be considered as starting at the end of the previous one. This default timestamp can be editted thanks to the first_file_begin parameter.
An Instrument can be provided to the Dataset for the WAV data to be converted in pressure units. This will lead the resulting spectra to be expressed in dB SPL (rather than in dB FS).
from pathlib import Path
audio_folder = Path(r"_static/sample_audio/id")
from osekit.public_api.dataset import Dataset
from osekit.core_api.instrument import Instrument
dataset = Dataset(
folder=audio_folder,
strptime_format=None,
instrument=Instrument(end_to_end_db=165.0),
)
dataset.build()
2026-02-04 15:57:58,837
Building the dataset...
2026-02-04 15:57:58,838
Analyzing original audio files...
2026-02-04 15:57:58,844
Organizing dataset folder...
2026-02-04 15:57:58,846
Build done!
The Public API Dataset is now analyzed and organized:
print(f"{' DATASET ':#^60}")
print(f"{'Begin:':<30}{str(dataset.origin_dataset.begin):>30}")
print(f"{'End:':<30}{str(dataset.origin_dataset.end):>30}")
print(f"{'Sample rate:':<30}{str(dataset.origin_dataset.sample_rate):>30}\n")
print(f"{' ORIGINAL FILES ':#^60}")
import pandas as pd
pd.DataFrame(
[
{
"Name": f.path.name,
"Begin": f.begin,
"End": f.end,
"Sample Rate": f.sample_rate,
}
for f in dataset.origin_files
],
).set_index("Name")
######################### DATASET ##########################
Begin: 2020-01-01 00:00:00
End: 2020-01-01 00:01:30
Sample rate: 48000
###################### ORIGINAL FILES ######################
| Begin | End | Sample Rate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | |||
| 1829.wav | 2020-01-01 00:00:00 | 2020-01-01 00:00:10 | 48000 |
| 1830.wav | 2020-01-01 00:00:10 | 2020-01-01 00:00:20 | 48000 |
| 1832.wav | 2020-01-01 00:00:20 | 2020-01-01 00:00:30 | 48000 |
| 1833.wav | 2020-01-01 00:00:30 | 2020-01-01 00:00:40 | 48000 |
| 1834.wav | 2020-01-01 00:00:40 | 2020-01-01 00:00:50 | 48000 |
| 1835.wav | 2020-01-01 00:00:50 | 2020-01-01 00:01:00 | 48000 |
| 1836.wav | 2020-01-01 00:01:00 | 2020-01-01 00:01:10 | 48000 |
| 1837.wav | 2020-01-01 00:01:10 | 2020-01-01 00:01:20 | 48000 |
| 1838.wav | 2020-01-01 00:01:20 | 2020-01-01 00:01:30 | 48000 |
Since we will run a spectral analysis, we need to define the FFT parameters:
from scipy.signal import ShortTimeFFT
from scipy.signal.windows import hamming
sample_rate = 24_000
sft = ShortTimeFFT(win=hamming(1024), hop=128, fs=sample_rate)
To run analyses in the Public API, use the Analysis class:
from osekit.public_api.analysis import Analysis, AnalysisType
from osekit.utils.audio_utils import Normalization
analysis = Analysis(
AnalysisType.SPECTROGRAM,
mode="files", # We want one spectrogram per file
sample_rate=sample_rate,
normalization=Normalization.DC_REJECT,
fft=sft,
v_lim=(0.0, 150.0), # Boundaries of the spectrograms
colormap="viridis", # Default value
name="8s_long_spectros",
)
The Core API can still be used on top of the Public API.
We’ll access the Core API SpectroDataset that match this analysis to trim and rename the exported spectrograms:
from pandas import Timedelta
spectro_dataset = dataset.get_analysis_spectrodataset(analysis)
for sd in spectro_dataset.data:
sd.name = next(iter(sd.audio_data.files)).path.stem
sd.end = sd.begin + Timedelta(seconds=8)
2026-02-04 15:57:58,879
Creating the audio data...
We can also glance at the spectrogram results with the Core API:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 1)
spectro_dataset.data[0].plot(ax=axs[1])
spectro_dataset.data[1].plot(ax=axs[0])
axs[0].get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
plt.show()
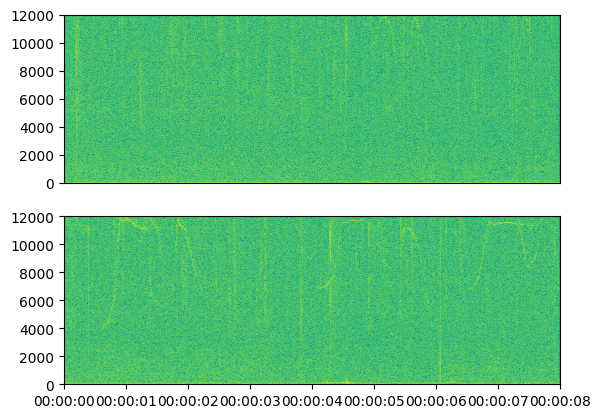
Running the analysis while specifying the filtered audio_dataset will skip the empty AudioData (and thus the empty SpectroData).
dataset.run_analysis(analysis=analysis, spectro_dataset=spectro_dataset)
2026-02-04 15:57:59,314
Creating the audio data...
2026-02-04 15:57:59,320
Running analysis...
2026-02-04 15:57:59,320
Computing and writing spectrograms...
2026-02-04 15:58:04,264
Analysis done!
All the new files from the analysis are stored in a SpectroDataset named after analysis.name:
pd.DataFrame(
[
{
"Exported file": path.name,
}
for path in (
audio_folder / "processed" / analysis.name / "spectrogram"
).iterdir()
],
).set_index("Exported file")
| Exported file |
|---|
| 1838.png |
| 1834.png |
| 1829.png |
| 1833.png |
| 1830.png |
| 1837.png |
| 1835.png |
| 1832.png |
| 1836.png |
